A significant development in the area of malignancy treatment has emerged as the lorlatinib first therapy.This new development medicine, which has the potential to revolutionize the approach of malignancy doctors to the beginning phases of malignancy treatment, represents a major development.Targeting specific biochemical processes, the lorlatinib first therapy offers a hopeful option to conventional chemotherapy, providing patients with a more efficient and less harmful treatment options.
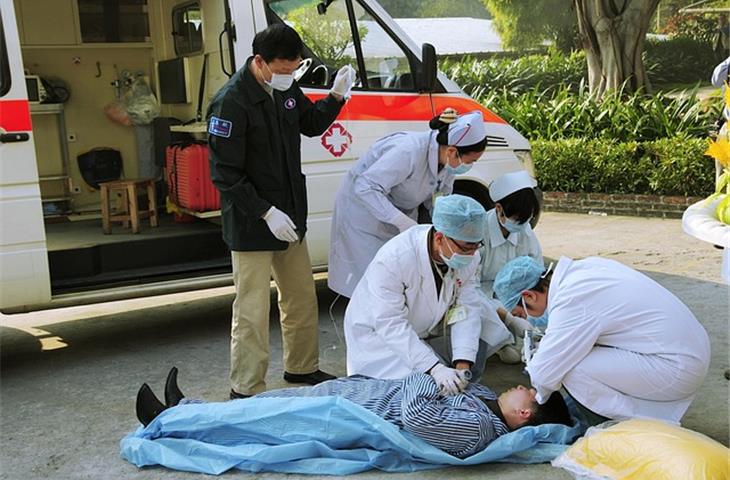

The new tyrosine kinase inhibiter (TKI) known as lorlatinib specifically inhibits the activity of certain malignancy-promoting enzymes.It primarily targets the alk (alk) and met, frequently altered in several malignancy types, such as lung, breast, and digestive system tumors.
Effective in halting the expansion and proliferation of tumor cells by inhibiting these receptors, lorlatinib first therapy leads to tumor reduction and improved patient results.The term ‘first stage treatment’ refers to the first stage treatment that is administered to a patient who has a newly diagnosed malignancy.It plays a crucial role in illness management and in improving general survival chances.
Selecting the appropriate initial therapy is crucial, as it can influence both the path of the illness and the patient’s well-being.For oncologists, lorlatinib as first-line treatment provides an attractive alternative, providing a precise and less harmful strategy than conventional chemotherapy.Remarkable efficacy in the management of lung cancer, particularly in patients with advanced or metastatic ALK-positive adenocarcinoma of the lung (NSCLC), has been proven by lorlatinib as first-line treatment.
lorlatinib as first-line treatment has considerably enhanced disease-free survival (PFS) and overall survival rate (OS), as proven by studies, when compared with standard care chemotherapy.Mainly investigated in lung cancer, the capacity for lorlatinib as first-line treatment applies to other types of cancer as well.initial studies indicates that lorlatinib may also be effective for treating ALK-positive invasive breast cancer and c-Met-overexpressing gastrointestinal malignancies.
Additional research are in progress to investigate the possibility the promise of lorlatinib for these purposes, and encouraging outcomes suggest a broad spectrum of uses for the initial use of lorlatinib.Providing a targeted and less harmful alternative to conventional conventional traditional chemotherapy, initial lorlatinib represents a major advance in the treatment of cancer.
Its capability to block particular cancer-causing kinases, including ALK and c-Met, has demonstrated considerable efficacy in lung treatment for cancer and offers promise for different cancer types.As research ongoing to evolve, initial lorlatinib is set to transform the strategy to the early stages of treatment for cancer, enhancing patient prognosis and improving their overall quality of life.
